Richard Dawkins’ concept of the “replicator” in his book “The Selfish Gene” provides a fascinating lens through which we can view the rise of Robotic Process Automation (RPA).
In the book, Dawkins argues that genes, not organisms, are the true “replicators” in evolution. These self-replicating molecules carry the instructions for building and maintaining life.
They are the fundamental units of natural selection, constantly undergoing mutation and replication. The success of a gene is measured by its ability to be copied and passed on to future generations.
Here’s the parallel to RPA: Like genes, RPA bots act as simple replicators in the automation world. They are programmed to mimic and repeat basic tasks with high accuracy and speed.
This ability to self-replicate a specific task lays the foundation for more sophisticated automation processes. Just as genes combine to form complex organisms, multiple RPA bots working together can automate entire workflows.
Think of it like this: Imagine a single gene coding for basic eye function. By itself, it’s a simple replicator. But combined with other genes, it contributes to the development of a complex visual system.
Similarly, a single RPA bot might automate data entry. But when combined with other bots, it can automate an entire customer onboarding process.
Both replicators and RPA represent a crucial starting point. They are the fundamental building blocks for future advancements. The replicator kicked off the evolutionary journey that led to complex life forms. RPA, in a similar way, is paving the way for intelligent automation.
As RPA technology evolves, it has the potential to revolutionize how work gets done, potentially automating not just basic tasks, but also more complex decision-making processes.
How does RPA factor into the evolution of an organization?
Organizations, like complex organisms, can suffer from internal time lags that hinder progress. This happens when critical functions operate at different speeds, creating bottlenecks and hindering overall agility.
A prime culprit? Rote tasks. Imagine this scenario:
- The CEO champions a bold initiative for a company transformation.
- But the sales team, bogged down by manual inventory tracking, lacks the bandwidth to adapt.
- Meanwhile, the product team is drowning in repetitive manual testing, resembling a fire brigade constantly putting out small fires.
This reactive, “firefighting” approach is the antithesis of Eric Ries’ Lean Startup methodology, which emphasizes iterative development and rapid adaptation. In this time-lagged state, innovative initiatives get sidelined while resources are consumed by repetitive tasks.

Breaking the Cycle
To address this, organizations need to streamline repetitive tasks through automation or process optimization. This frees up valuable time and cognitive energy, allowing teams to focus on strategic initiatives and innovative problem-solving.
By tackling time lag, organizations can move from firefighting to a more proactive, adaptive model, fostering innovation and accelerating growth.
And this is where RPA comes in.
Basically, what we are talking about here is automating any kind of task that gets in the way of human ingenuity, or those tasks that do not lead to it. When you approach a business problem from the lens of RPA, the amount of things you can automate is virtually endless.
Imagine somebody operating your computer screen, the mouse moves from one page to another, types in a search query on Google, clicks on a particular result, and collects the required data. Only that the person who is supposed to be doing this does not exist!
The Basics of RPA
All a task needs to have it automated are the following criteria:
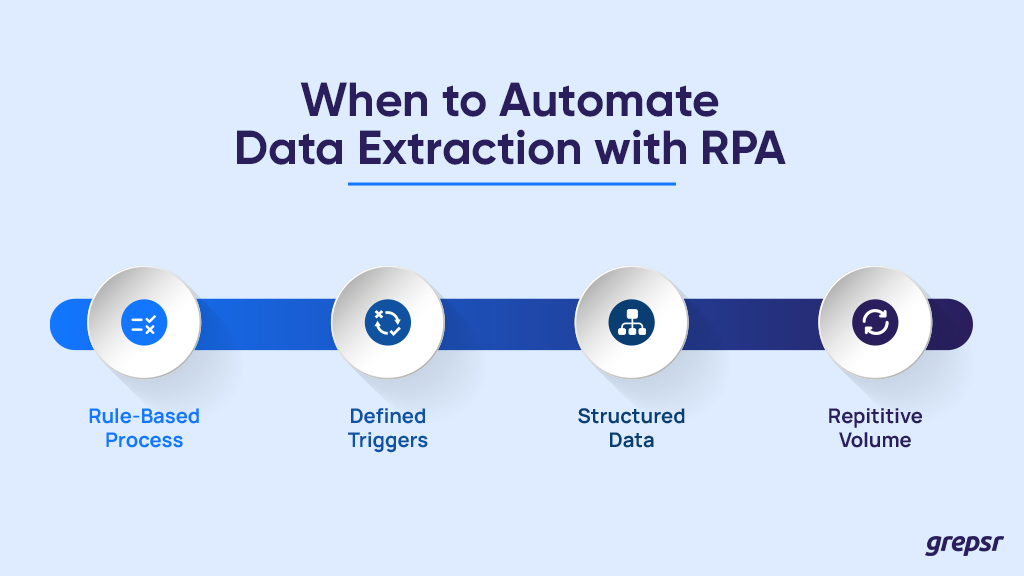
When these criteria are met, you can get started on your RPA edge case.
RPA is a replicator. While traditional automation focused solely on simple automations like filling in documents, and generating reports, with the advancement in AI, and development of intuitive chatbots, RPA is no longer restricted to performing rote tasks.
It can aid in carrying out complex customer query handling. Say, a customer is looking for a particular file, or data. A chatbot can use NLP (Natural Language Processing) to understand customer needs, but it can converse with the customer based only on the data available in its repertoire.
When you integrate an RPA bot in legacy systems (which can be done on-site or through the cloud), and you do not need APIs between the systems to implement the bot, a trigger signal from the chatbot can send the bot on a quest to find the data the client is looking for.
What’s more? The bot can traverse through multiple systems and fetch the data demanded by the customer.
RPA is a force multiplier that when embedded with AI, can create a scalable component in your organization, something that can establish a virtuous cycle, leading to exponential growth.
Beyond Efficiency: RPA for Intelligent Automation Across Industries
Once you have the fundamentals sorted out, the amount of functions where you can implement RPA is virtually limitless. In this section, we will cover some areas where RPA is being implemented with AI, leading to intelligent process automation.
1. Financial Risk Management
Financial management carries inherent risks, even in fundamental aspects like accounts receivables and payable.
- Accounts Receivable: Manual invoice processing can become a time drain, especially with high transaction volumes. Here, RPA shines. It automates tasks like collecting, processing, and storing invoices, freeing up employee time for more strategic activities.
- Accounts Payable: RPA bots can be programmed to trigger automated payments based on predefined criteria, (e.g., reaching a specific date or discount eligibility) ensuring timely payments to vendors and potentially capturing early payment discounts.
The Power of combining RPA with AI
RPA excels at following predefined rules, but AI adds a new layer of intelligence. This empowers financial systems to proactively manage risk. Here’s an example:
Dual Automation Approach: Implement a two-pronged strategy. Let RPA bots handle invoice processing while AI continuously monitors the process for anomalies. This can involve anomaly detection algorithms to identify suspicious invoices or payment patterns, flagging potential fraud attempts.
2. Competitive Analysis
E-commerce thrives on dynamic pricing strategies. To stay ahead, businesses must continuously monitor competitor pricing, supplier costs, and even indirect competition.
Traditionally, this involved manual data extraction, a tedious and error-prone process. RPA offers a powerful selection:
- Automated Data Extraction: RPA bots actively access competitor websites at regular intervals, extracting key data points like pricing information, customer reviews, and product details.
- Streamlined Data Processing: Our system automatically parses the extracted data and feeds it into our client’s database, eliminating manual data entry and ensuring data accuracy.
- Data Visualization for Informed Decisions: You can transform the collected data into insightful visualizations, empowering you to swiftly identify pricing trends and adapt your own strategies accordingly.
3. Chatbot Augmentation
Chatbots play a crucial role in sales prospecting by qualifying leads. They engage with potential customers, understand their needs, and determine their suitability for further sales efforts. However, a chatbot’s effectiveness is limited by its access to data.
The Challenge: Siloed Data Hinders Chatbot Performance
Often, critical customer information resides in disparate databases across the organization. This siloed data creates a barrier for chatbots, hindering their ability to provide comprehensive answers to customer inquiries.
The Solution: RPA to the Rescue
Robotic Process Automation (RPA) bridges the data gap by:
- Accessing Data from Multiple Sources: RPA seamlessly retrieves data from various internal systems, including legacy applications, eliminating the need for complex API integrations.
- Extracting Relevant Information: RPA actively extracts the specific data requested by the customer, ensuring accurate and timely responses.
4. Strategic Change Management
The software industry, like surfing, requires constant adaptation to new waves (trends) and technologies. Disintermediation is a continuous threat, necessitating strategic change management. Companies must periodically re-evaluate business models, streamline processes, and embrace innovation to stay afloat.
A Framework for Navigating Change
One common framework outlines four key concepts for structural organizational change:
- Automation: Utilizing technology to eliminate manual tasks, improving efficiency.
- Rationalization: Streamlining existing processes to reduce redundancies and optimize workflows.
- Redesign: Fundamentally rethinking business processes to create entirely new and improved ways of working.
- Paradigm Shifts: Introducing disruptive innovations that completely change the game and potentially redefine the industry.
RPA: A Stepping Stone for Transformation
Within this framework, RPA falls under automation. While it offers a lower risk-reward profile compared to redesign or paradigm shifts, its impact shouldn’t be underestimated. RPA acts as a stepping stone for more transformative changes:
- Efficiency Gains: Automating repetitive tasks frees up human resources for higher-value activities, fostering innovation and strategic thinking.
- Process Optimization: RPA streamlines workflows, creating a foundation for more complex process redesign initiatives.
- Data Visibility: RPA can improve data capture and accessibility, providing valuable insights for data-driven decision-making.
RPA, though categorized as low-risk, low-reward within the framework, plays a crucial role in strategic change management.
It lays the groundwork for further automation, process optimization, and data-driven decision making, ultimately paving the way for more substantial transformations that keep businesses competitive in the ever-evolving landscape.
RPA and Data Extraction: A Case Study in Customer Service Innovation
Client: TechX, an Electronic E-commerce Store
Use Case: Combating the Competitor’s Edge
Challenge: TechX wanted to up their customer service game by analyzing competitor AI responses to TV-related questions on Amazon mobile apps. However, directly accessing competitor mobile app data for TVs posed challenges.
Our Solution: We built an API endpoint for TechX. By inputting specific TV models and questions, they triggered a RPA workflow that extracted a competitor’s mobile app (e.g., mega mart) to retrieve AI-generated responses for those queries.
Principle Challenges
- Limited Accessibility: Mobile apps often restrict access to underlying data like AI responses. Public APIs for competitor AI specifically on TVs might not be readily available.
- The UI Labyrinth: Mobile apps can employ anti-bot measures like device fingerprinting to detect scraping attempts.
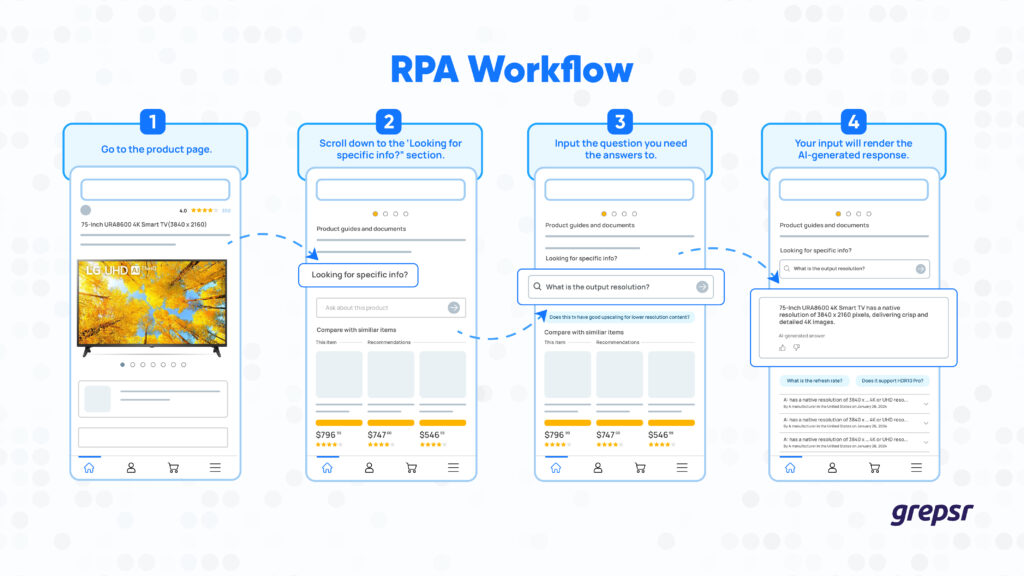
While we can’t disclose the specifics of our client’s use of competitor chatbot responses, this data extraction workflow offers a valuable advantage. It allows you to gain insights into how competitors’ chatbots respond to queries. With this knowledge, you can improve your own chatbot’s responses and provide exceptional customer service.
In a hyper-competitive business environment with razor-thin profit margins, getting even a slight competitive advantage is a massive gain.
You could serve your customers better this way.
Not only did this approach offer a cost-effective solution for data extraction, even within the confines of mobile applications, but it also provided TechX with a comprehensive means to monitor and understand their competitor’s customer service operations.
Implement RPA to Evolve
In both the realm of biology and business, the path to significant growth and success hinges on the development of scalable components or mechanisms capable of amplifying essential functions. Typically, this scalability emerges through extensive repetition and refinement.
Robotic Process Automation (RPA) stands out as a prime example of such a replicator in the modern business landscape. By harnessing the synergy of RPA bots with Artificial Intelligence (AI), organizations can unlock unparalleled efficiency gains, propelling them into a new era of automation and productivity.
Implementing RPA in data extraction is not just about automating mundane tasks; it’s about empowering your organization to achieve the extraordinary.
Your employees are freed from the shackles of repetitive work, allowing them to unleash their creativity and strategic thinking. RPA and data extraction can be your force-multiplier, propelling your organization towards a future brimming with possibilities.
The case study of TechX exemplifies the potential of RPA. By harnessing its power, they gained a crucial edge in a crowded and competitive landscape, ultimately enhancing their customer service. Yet, this is just a glimpse of what RPA can achieve.
The future is bright. As RPA continues to evolve alongside advancements in AI, its capabilities will become even more sophisticated. The possibilities are truly endless.
So, embrace RPA. Let it be the replicator that ushers in a new era of growth and innovation for your organization. With RPA firmly embedded in your workflow, there’s no limit to what you can accomplish.